Chapter 10 Histograms
10.1 Introduction
In this chapter, we will learn to
- build histogram
- specify bins
- modify
- color
- fill
- alpha
- bin width
- line type
- line size
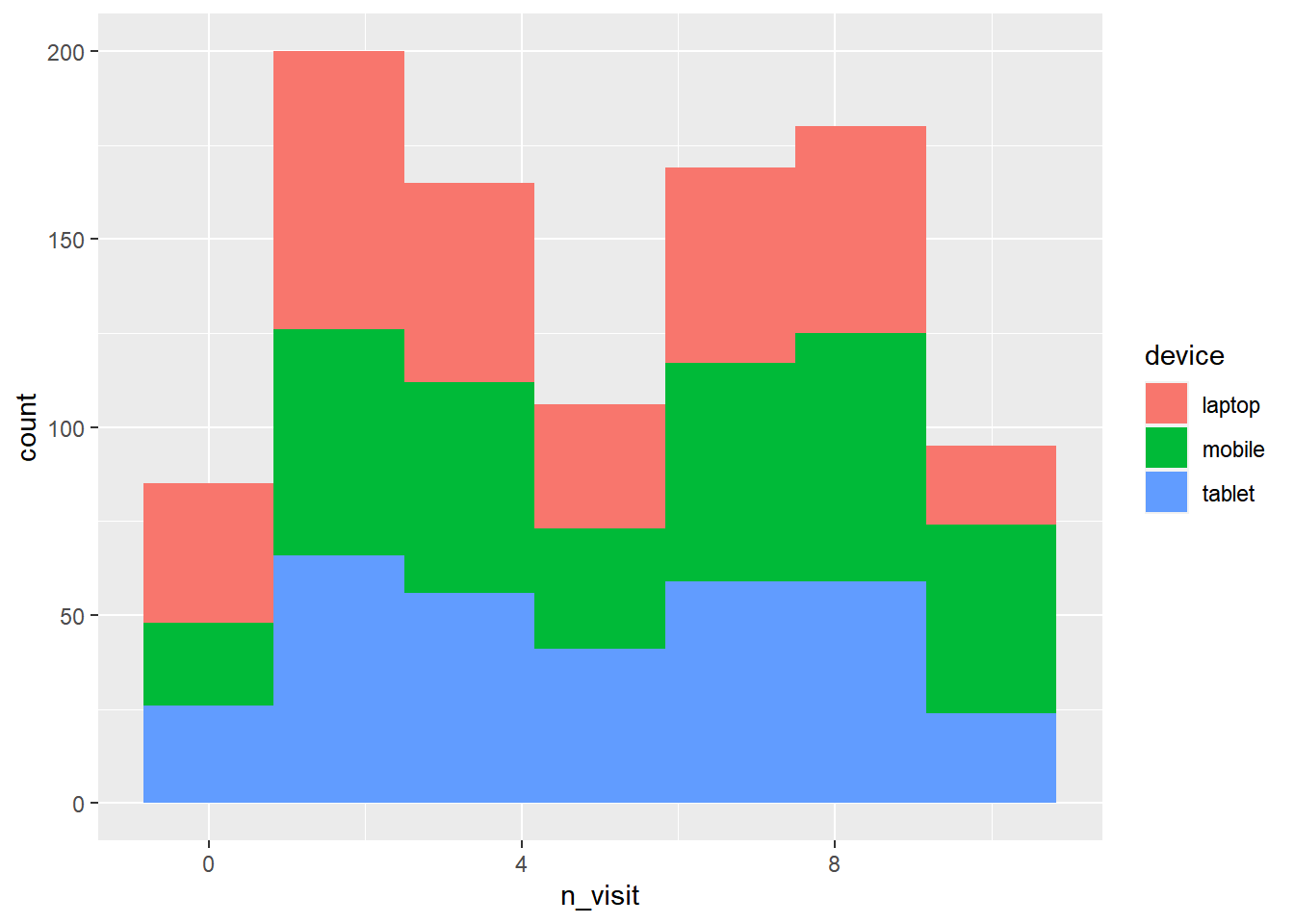
- map aesthetics to variables
A histogram is a plot that can be used to examine the shape and spread of continuous data. It looks very similar to a bar graph and can be used to detect outliers and skewness in data. The histogram graphically shows the following:
- center (location) of the data
- spread (dispersion) of the data
- skewness
- outliers
- presence of multiple modes
To construct a histogram, the data is split into intervals called bins. The intervals may or may not be equal sized. For each bin, the number of data points that fall into it are counted (frequency). The Y axis of the histogram represents the frequency and the X axis represents the variable.
10.2 Data
ecom <- readr::read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rsquaredacademy/datasets/master/web.csv')
ecom## # A tibble: 1,000 x 11
## id referrer device bouncers n_visit n_pages duration country purchase
## <dbl> <chr> <chr> <lgl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <lgl>
## 1 1 google laptop TRUE 10 1 693 Czech Repub~ FALSE
## 2 2 yahoo tablet TRUE 9 1 459 Yemen FALSE
## 3 3 direct laptop TRUE 0 1 996 Brazil FALSE
## 4 4 bing tablet FALSE 3 18 468 China TRUE
## 5 5 yahoo mobile TRUE 9 1 955 Poland FALSE
## 6 6 yahoo laptop FALSE 5 5 135 South Africa FALSE
## 7 7 yahoo mobile TRUE 10 1 75 Bangladesh FALSE
## 8 8 direct mobile TRUE 10 1 908 Indonesia FALSE
## 9 9 bing mobile FALSE 3 19 209 Netherlands FALSE
## 10 10 google mobile TRUE 6 1 208 Czech Repub~ FALSE
## # ... with 990 more rows, and 2 more variables: order_items <dbl>,
## # order_value <dbl>10.2.1 Data Dictionary
- id: row id
- referrer: referrer website/search engine
- os: operating system
- browser: browser
- device: device used to visit the website
- n_pages: number of pages visited
- duration: time spent on the website (in seconds)
- repeat: frequency of visits
- country: country of origin
- purchase: whether visitor purchased
- order_value: order value of visitor (in dollars)
10.3 Plot
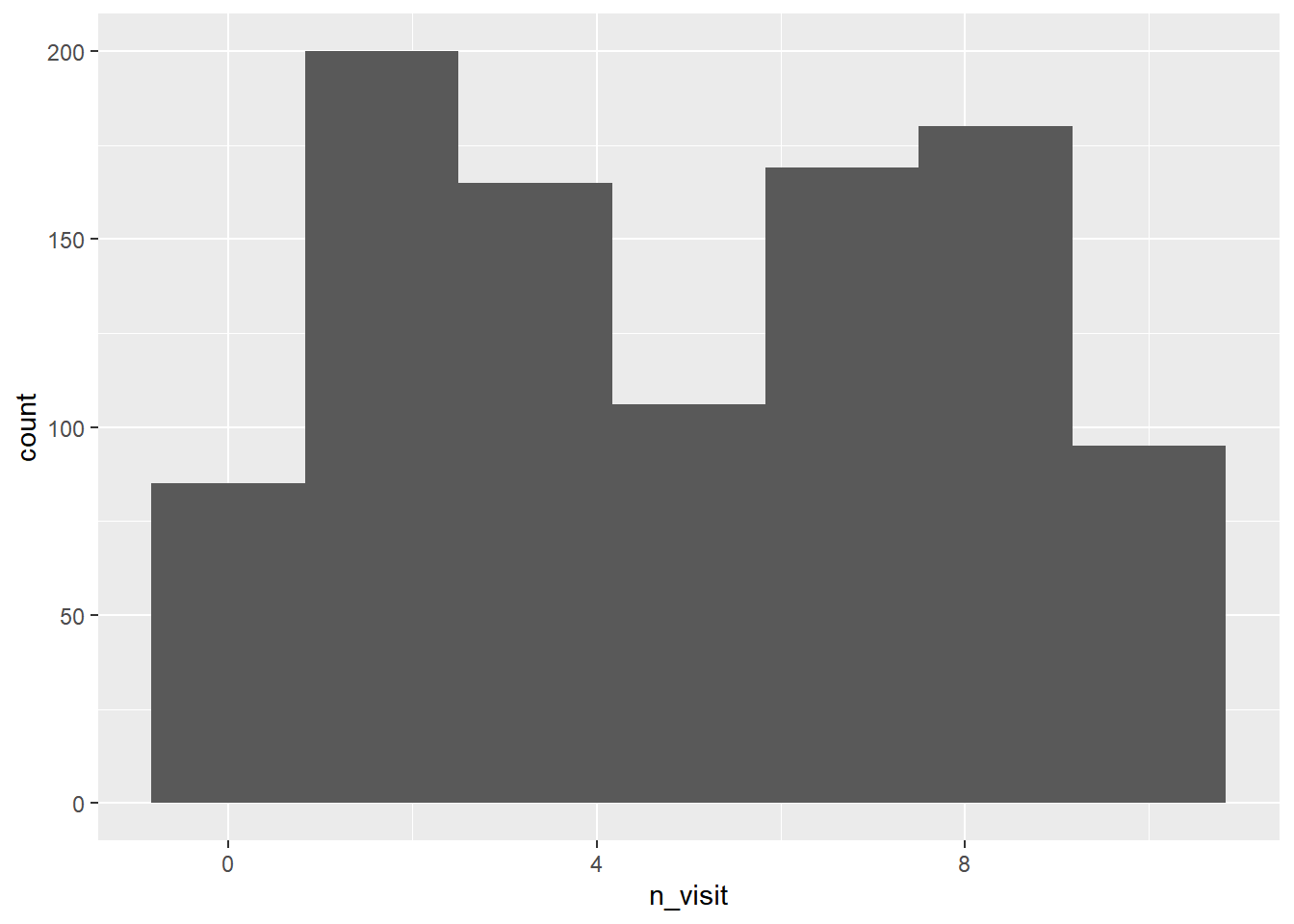
To create a histogram, we will use geom_histogram() and specify the variable
name within aes(). In the below example, we create histogram of the variable
n_visit.
ggplot(ecom) +
geom_histogram(aes(n_visit))## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.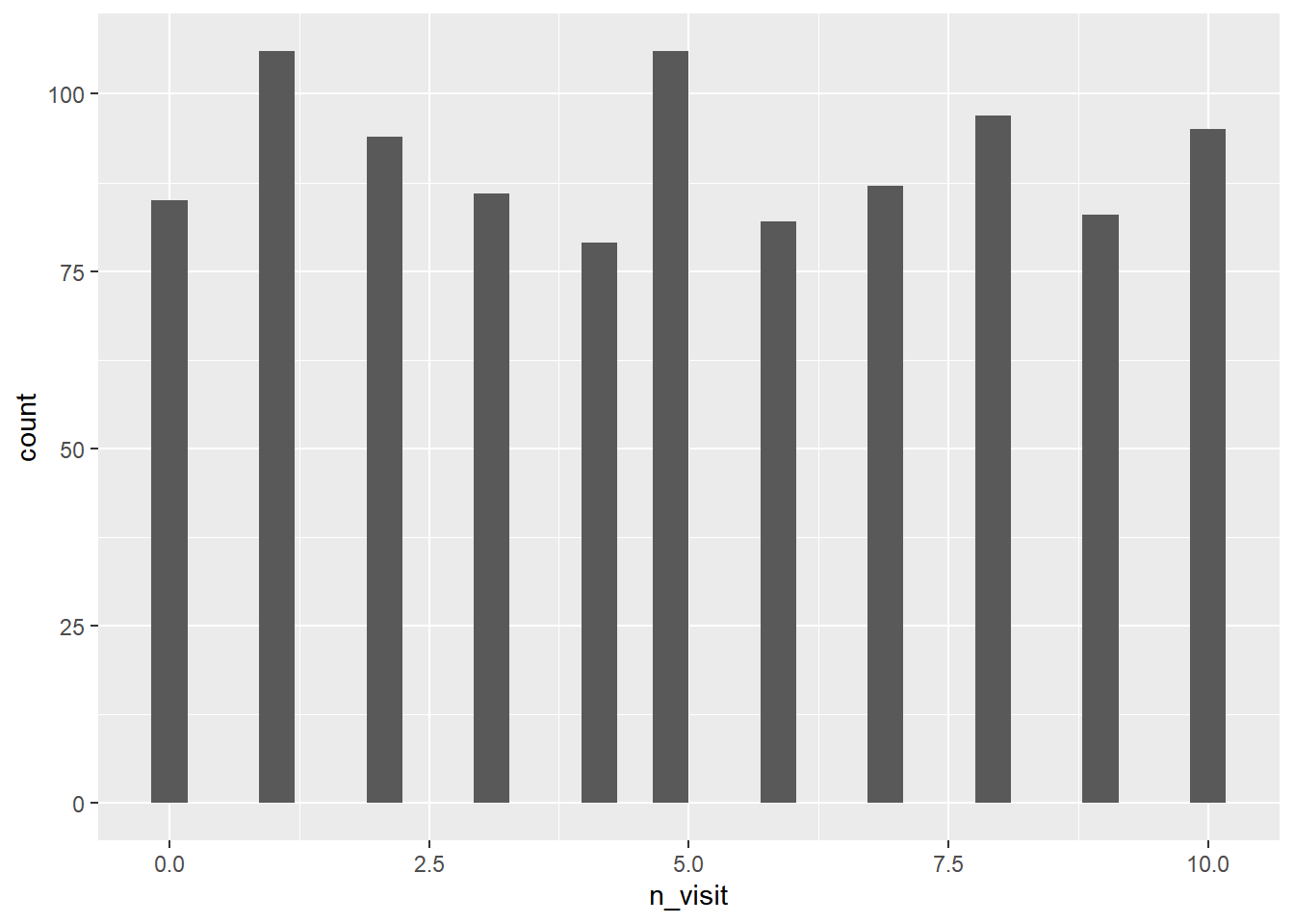
10.4 Aesthetics
Now that we know how to create a histogram, let us learn to modify its
appearance. We will begin with the background color. Use the fill argument
to modify the background color of the histogram. In the below case, we change
the color of the histogram to ‘blue’.
ggplot(ecom) +
geom_histogram(aes(n_visit), bins = 7, fill = 'blue')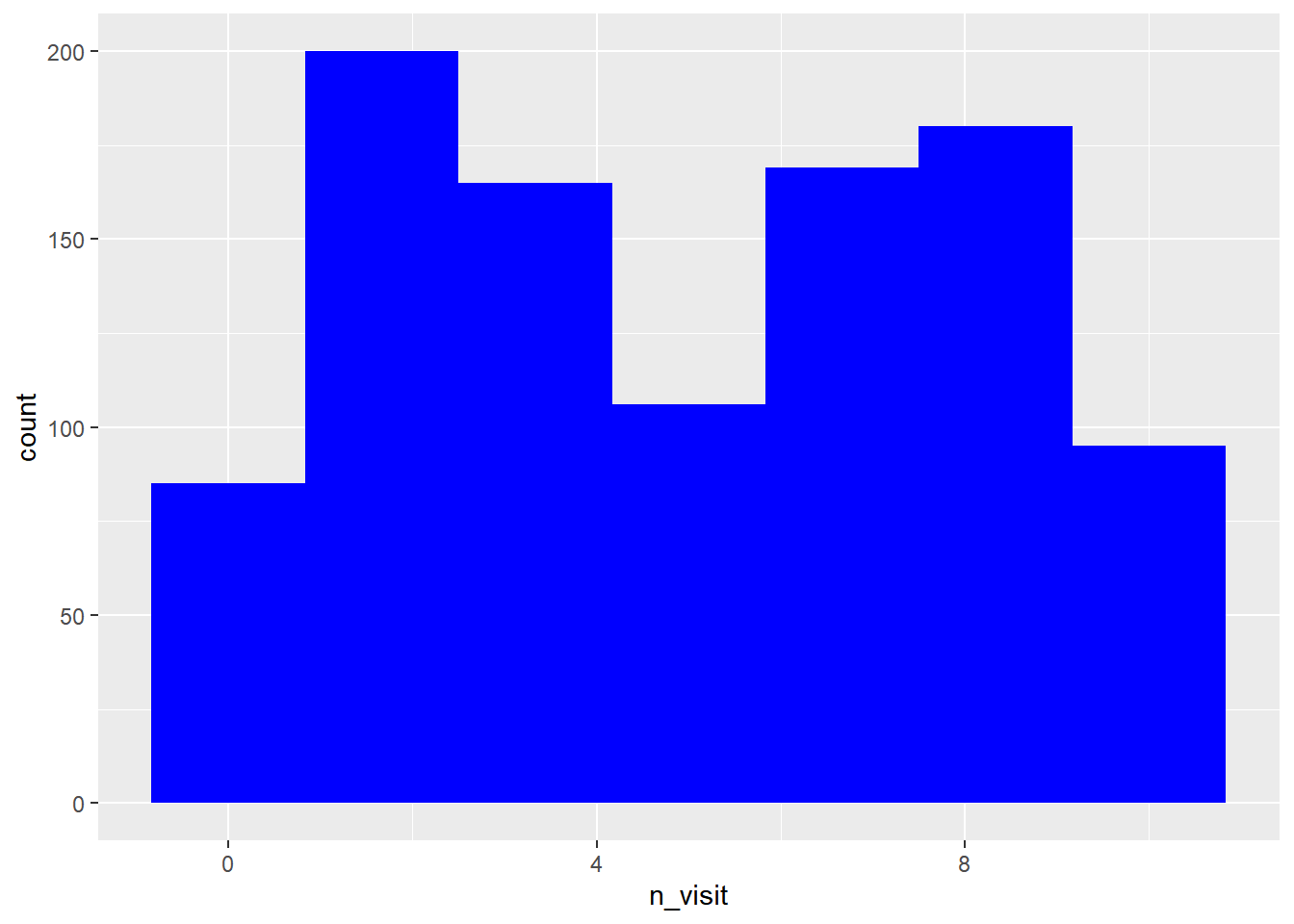
As we have learnt before, the transparency of the background color can be
modified using the alpha argument. It can take any value between 0 and 1.
ggplot(ecom) +
geom_histogram(aes(n_visit), bins = 7, fill = 'blue', alpha = 0.3)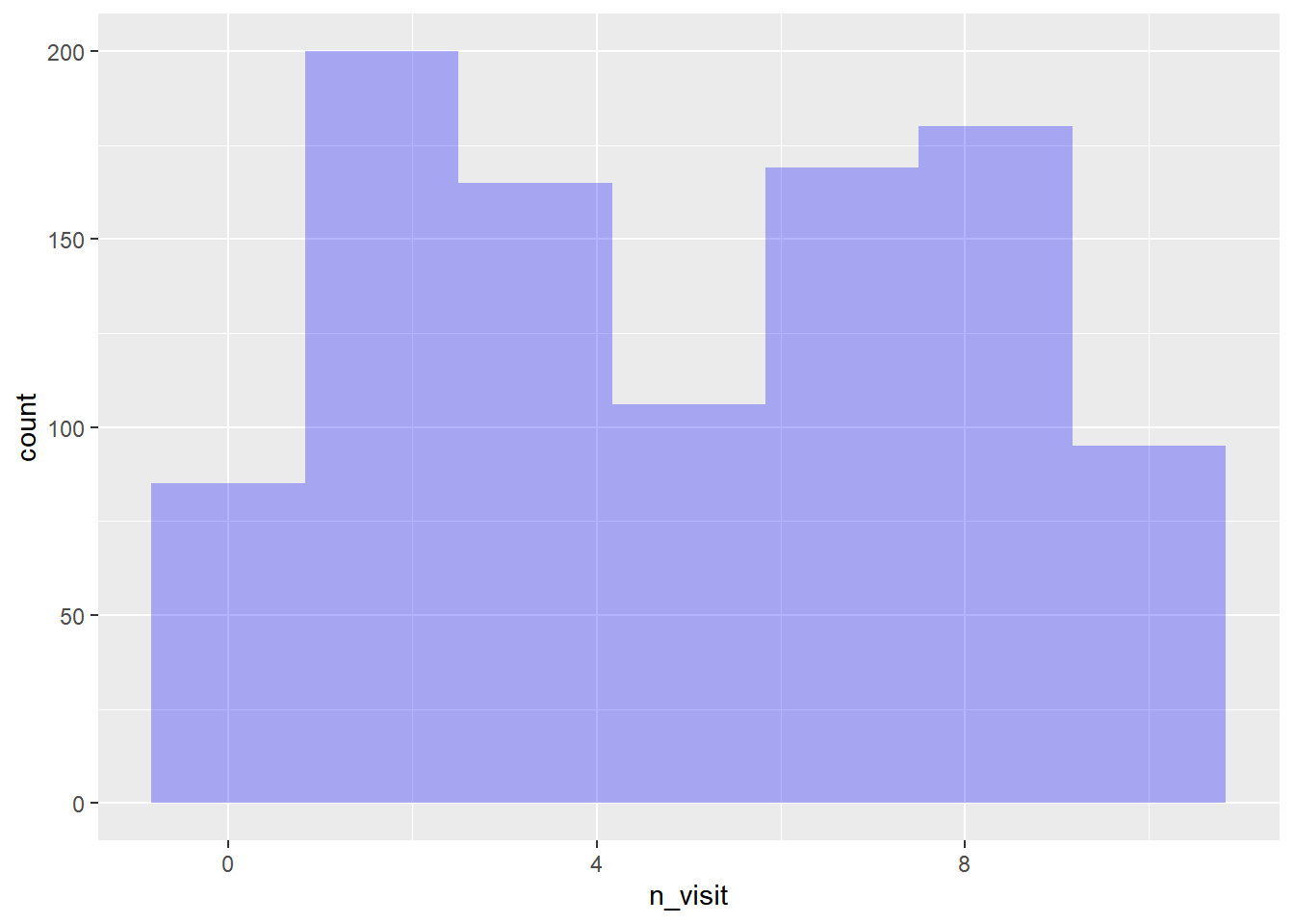
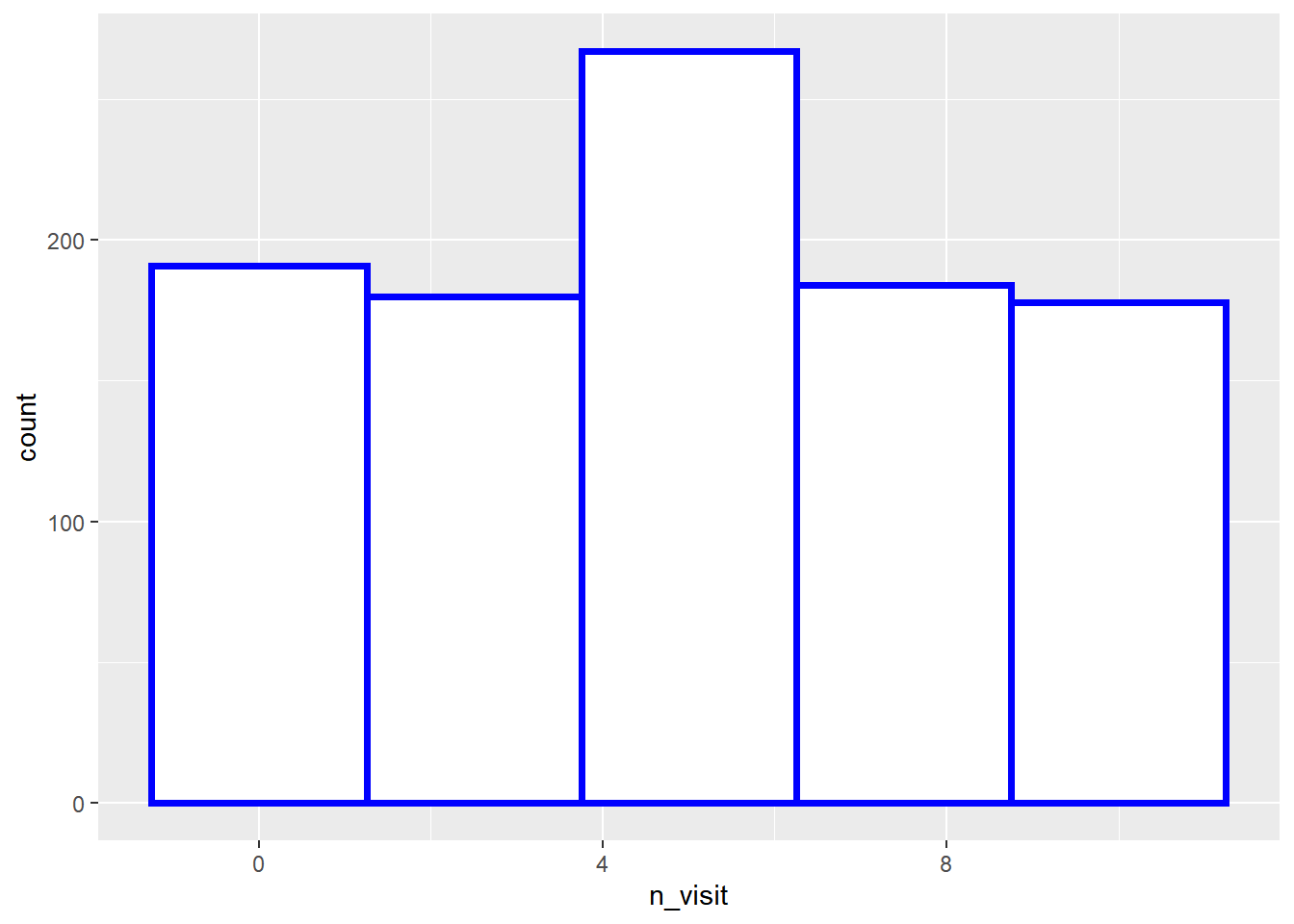
The color of the histogram border can be modified using the color argument.
The color can be specified either using its name or the associated hex code.
ggplot(ecom) +
geom_histogram(aes(n_visit), bins = 7, fill = 'white', color = 'blue')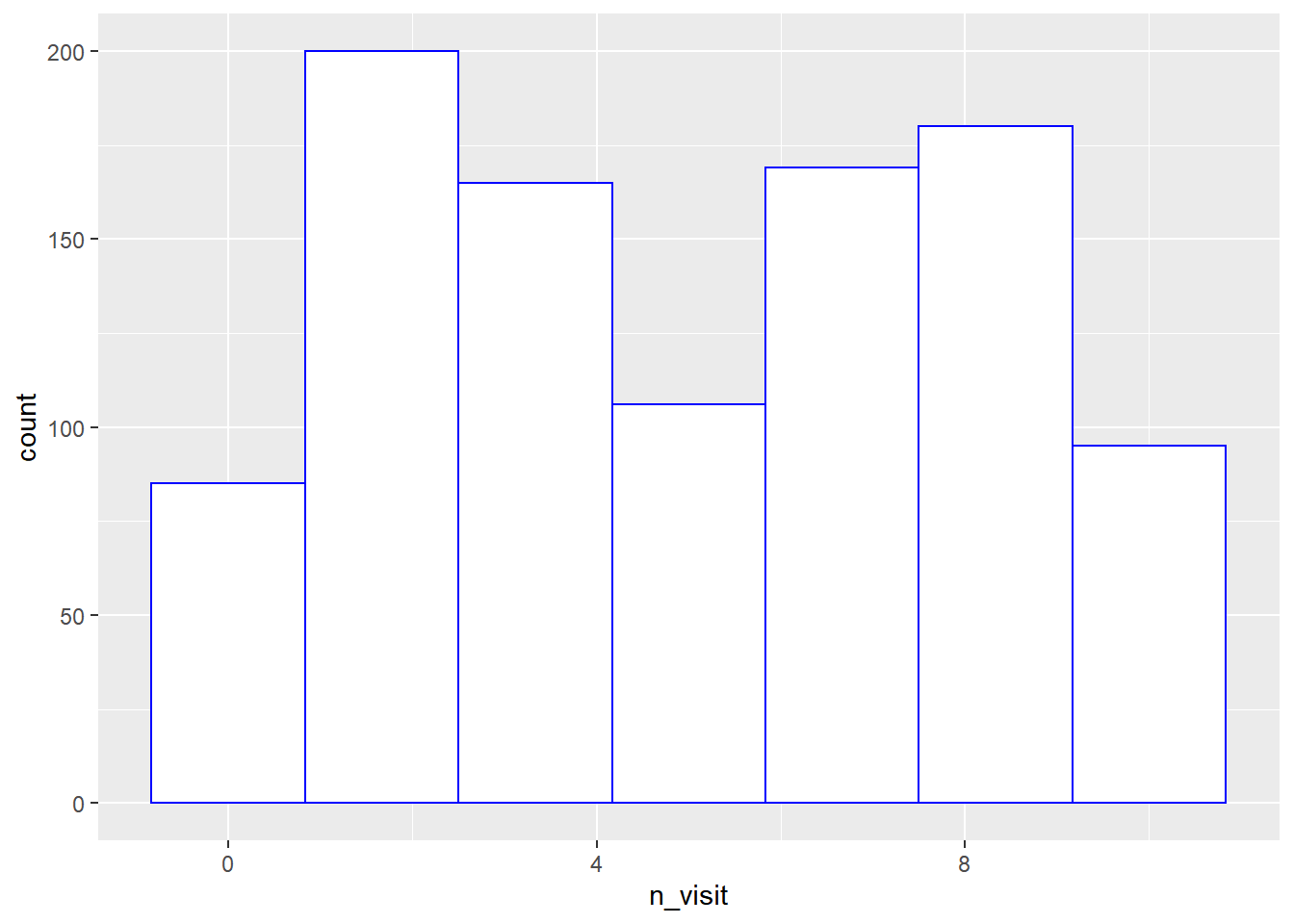
10.5 Putting it all together…
Let us modify the bins, the background and border color of the histogram in the below example.
ggplot(ecom) +
geom_histogram(aes(n_visit), bins = 7, fill = 'blue', color = 'white')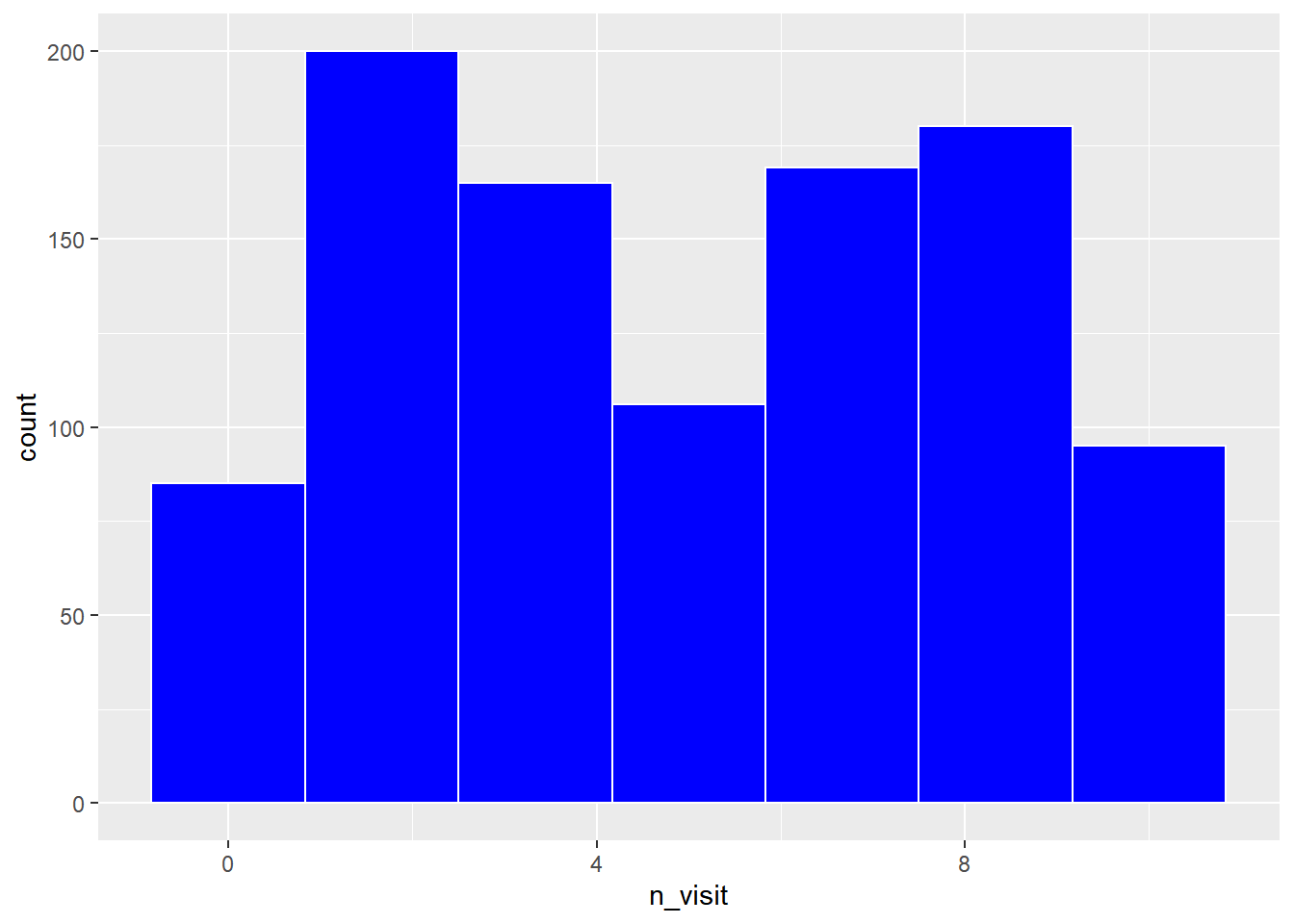
10.6 Bin Width
Another way to control the number of bins in a histogram is by using the
binwidth argument. In this case, we specify the width of the bins instead
of the number of bins. As you can see, in the below example, we do not use
the bins argument when using the binwidth argument. You can use either of
them but not both.
ggplot(ecom) +
geom_histogram(aes(n_visit), binwidth = 2, fill = 'blue', color = 'black')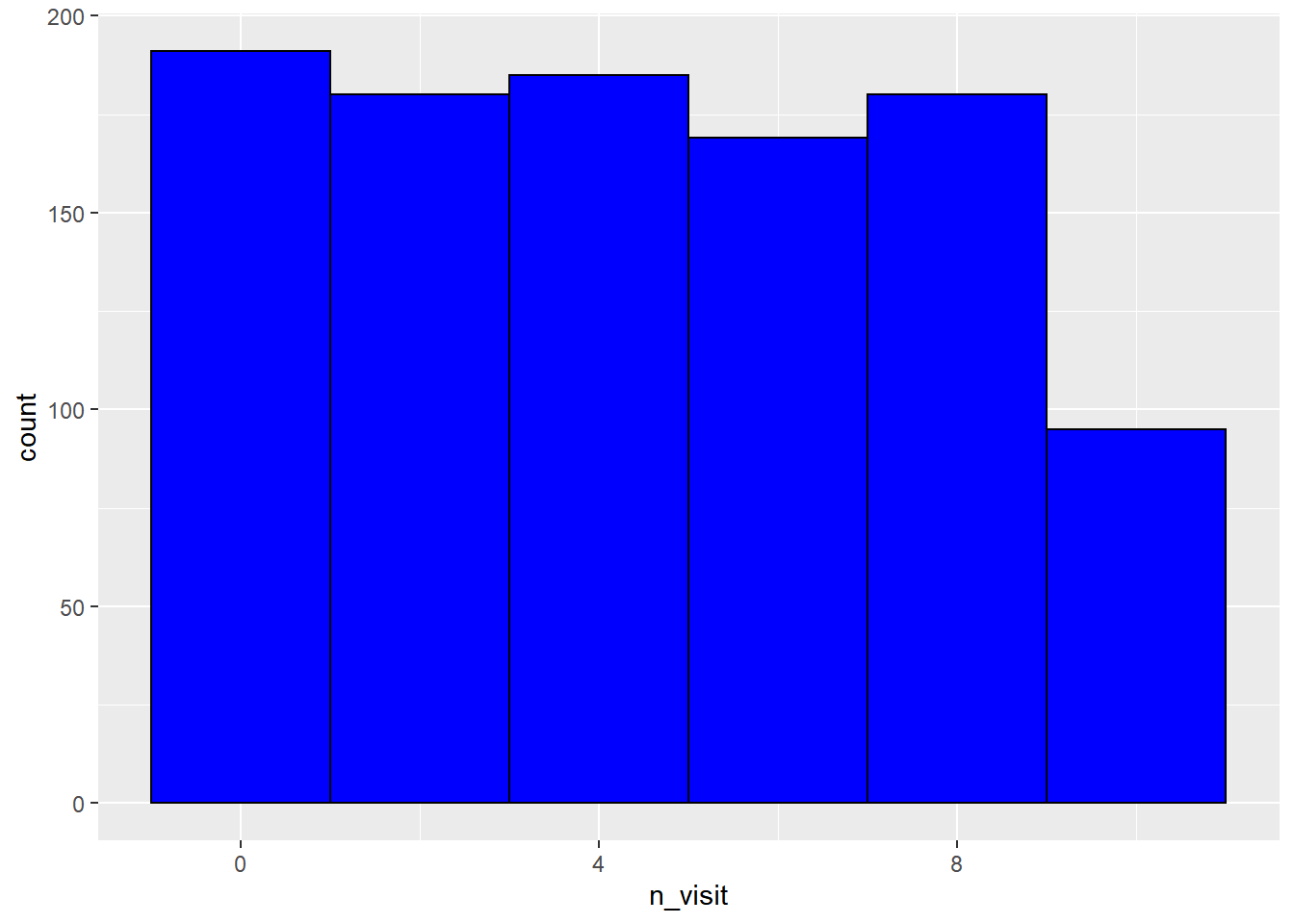
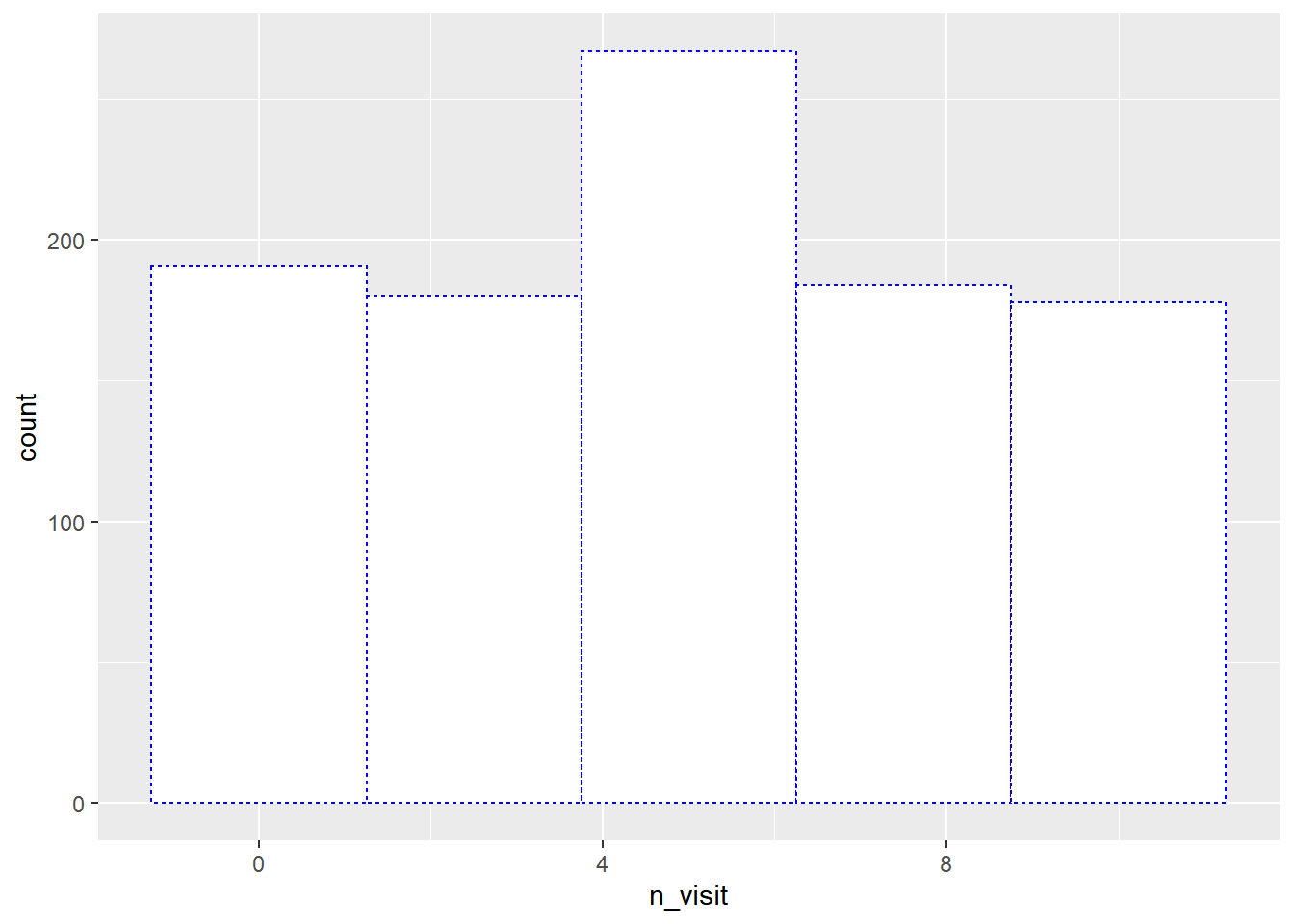
10.7 Line Type
The line type of the histogram border can be modified using the linetype
argument. It can take any integer value between 0 and 6.
ggplot(ecom) +
geom_histogram(aes(n_visit), bins = 5, fill = 'white',
color = 'blue', linetype = 3)